并查集
约 1514 字大约 5 分钟
并查集
概念
- 用于存储不相交的集合
- 可以高效支持两种操作
Find(x):返回 x 所属集合的“代表”Union(x, y): 合并包含 x 和 y 的两个集合
- 两种操作都可以在常量时间内完成
- 简单实现
- 主要思想:用有根树表示每个集合
- 每个节点都维护着一个到它的父节点的链接
- 根节点是对应集合的“代表”
- 例如: 两个集合
{x, y, z}and{a, b, c, d}
代码实现
int Find(int x) {
// 自己不是根节点,递归查找
while(x != L[x]) x = L[x];
return x;
}
void Union(int x, int y) {
// 直接连接
L[Find(x)] = Find(y);
}
Find(x)
- 跟随从 x 的连接直到一个节点指向自己,这可能需要 O(n) 时间,但我们会让它更快

- Quick-find,在查找时候直接返回
id[p]
public class QuickFindUF {
private int[] id; // id[i] = component identifier of i
private int count; // number of components
// 其他省略
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
return id[p];
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
validate(p);
validate(q);
int pID = id[p]; // needed for correctness
int qID = id[q]; // to reduce the number of array accesses
// p and q are already in the same component
if (pID == qID) return;
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
// 这里性能比较低,需要全部都修改
if (id[i] == pID) id[i] = qID;
count--;
}
}
Union(x, y)
- 运行 Find(x) 和 Find(y) 以找到对应的根节点并将一个指向另一个
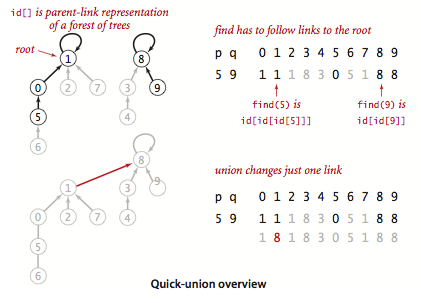
- Quick-union
public class QuickUnionUF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private int count; // number of components
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// 这里只变更了一个节点,所以需要变更的是根节点
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
count--;
}
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
}
Weighted quick-union
- 主要是将小子树挂到大子树上面
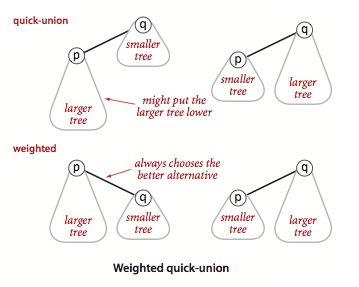
- 代码实现
public class WeightedQuickUnionUF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private int[] size; // size[i] = number of elements in subtree rooted at i
private int count; // number of components
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// 让小节点挂在到大节点上
// make smaller root point to larger one
if (size[rootP] < size[rootQ]) {
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
size[rootQ] += size[rootP];
}
else {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
size[rootP] += size[rootQ];
}
count--;
}
}
Path Compression
- 在糟糕的情况下,树可能会变得太深
- 这会减慢未来的运行速度
- 每次调用
Find()时,路径压缩都会使树变浅 - 只要根保持不变,我们不在乎树的样子
Find(x)返回根后,回溯到 x 并将所有链接重新路由到根
Path-Compression实现
我们将假设链接存储在 L[]
int Find(int x) {
if(x == L[x]) return x;
int root = Find(L[x]);
// 路径压缩
L[x] = root;
return root;
}
int Find(int x) {
return x == L[x] ? x : L[x] = Find(L[x]);
}
Java代码下载
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/edu.princeton.cs/algs4 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>edu.princeton.cs</groupId>
<artifactId>algs4</artifactId>
<version>1.0.4</version>
</dependency>
通用代码
- 设计数据结构
public class UF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private byte[] rank; // rank[i] = rank of subtree rooted at i (never more than 31)
private int count;
}
- 初始化数据
public UF(int n) {
if (n < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
rank = new byte[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 自己指向自己
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 0;
}
}
- 可以忽略不重要代码
// 判断索引
private void validate(int p) {
int n = parent.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= n) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n-1));
}
}
Find(x)代码
/**
* Returns the component identifier for the component containing site {@code p}.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @return the component identifier for the component containing site {@code p}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= p < n}
*/
public int find(int p) {
// 校验索引
validate(p);
// 如果当前元素的父亲不是自己,继续查找
while (p != parent[p]) {
// 路径压缩
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]; // path compression by halving
p = parent[p];
}
// 找到了根节点
return p;
}
Union(x, y)代码
/**
* Merges the component containing site {@code p} with the
* the component containing site {@code q}.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public void union(int p, int q) {
// 查找p的根
int rootP = find(p);
// 查找q的根
int rootQ = find(q);
// 如果相等,已经连接过了
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// 集合数量多的不变,少的将父亲指向多的
// make root of smaller rank point to root of larger rank
if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) parent[rootP] = rootQ;
else if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) parent[rootQ] = rootP;
else {
// 子树数量相等
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
// 等级+1
rank[rootP]++;
}
// 集合数量减1
count--;
}
Go实现
- 创建数据结构
type UF struct {
parent, rank []int
nComponents int
}
- 初始化数据结构
func newUF(initSize int) *UF {
// 初始化数据结构
uf := &UF{
parent: make([]int, initSize),
rank: make([]int, initSize),
nComponents: initSize,
}
// 子树等级初始化
for index := range uf.rank {
uf.rank[index] = 0
}
// 自己的父亲指向自己
for index := range uf.parent {
uf.rank[index] = index
}
return uf
}
- Find(x)
func (uf *UF) find(item int) int {
for item != uf.parent[item] {
// 路径压缩
uf.parent[item] = uf.parent[uf.parent[item]]
// 向上走
item = uf.parent[item]
}
return item
}
- Union(x, y)
func (uf *UF) merge(p, q int) {
// 查找p的根
rootP := uf.find(p)
// 查找q的根
rootQ := uf.find(q)
// 已经在一个集合里面了
if rootQ == rootP {
return
}
subTreeP := uf.rank[rootP]
subTreeQ := uf.rank[rootQ]
if subTreeP < subTreeQ {
uf.parent[rootP] = rootQ
} else if subTreeP > subTreeQ {
uf.parent[rootQ] = rootP
} else {
// 子树等级相同,使用那个都行
// uf.parent[rootP] = rootQ
// uf.parent[rootQ] = rootP
uf.parent[rootQ] = rootP
uf.rank[rootP]++
}
// 集合个数减少一个
uf.nComponents--
}
总结
- 核心思想为树,查找根节点
- 使用位运算也可以进行处理,例如Go程序设计语言 6.5 位向量代码