概念
约 2045 字大约 7 分钟
概念
- 一种抽象的方式表达节点(也叫顶点)和边的连接方式
- 我们使用1~n标记节点
- m条边连接一些节点
- 边可以是单向(有向)或双向
- 节点和边可以有一些辅助信息
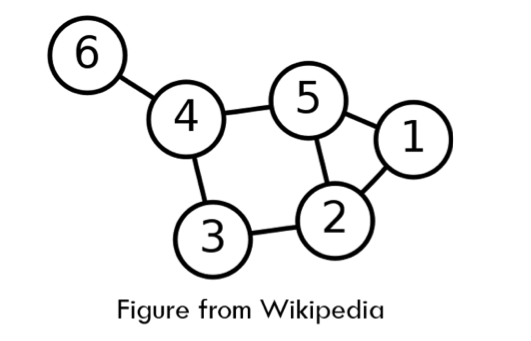
场景
- 最短路径问题
- 网络流量问题
- 匹配问题
2-SAT问题- 图着色问题
- 旅行商问题(TSP):仍未解决!
- 其他等等
术语
顶点
顶点,也就是节点
度
- 顶点的入度,表示有多少条边指向这个顶点
- 顶点的出度,表示有多少条边是以这个顶点为起点指向其他顶点
邻接
邻接,如果两个顶点被同一个边连接,就称这两个顶点是邻接的。
路径
路径,边的序列,例如图中显示了一条从 B 到顶点 J 的路径,这条路径通过了顶点 A 和顶点 E,这条路径叫做 BAEJ。这两个顶点之间还有其他路径,从 B 到 J 的另外一个路径是 BCDJ。
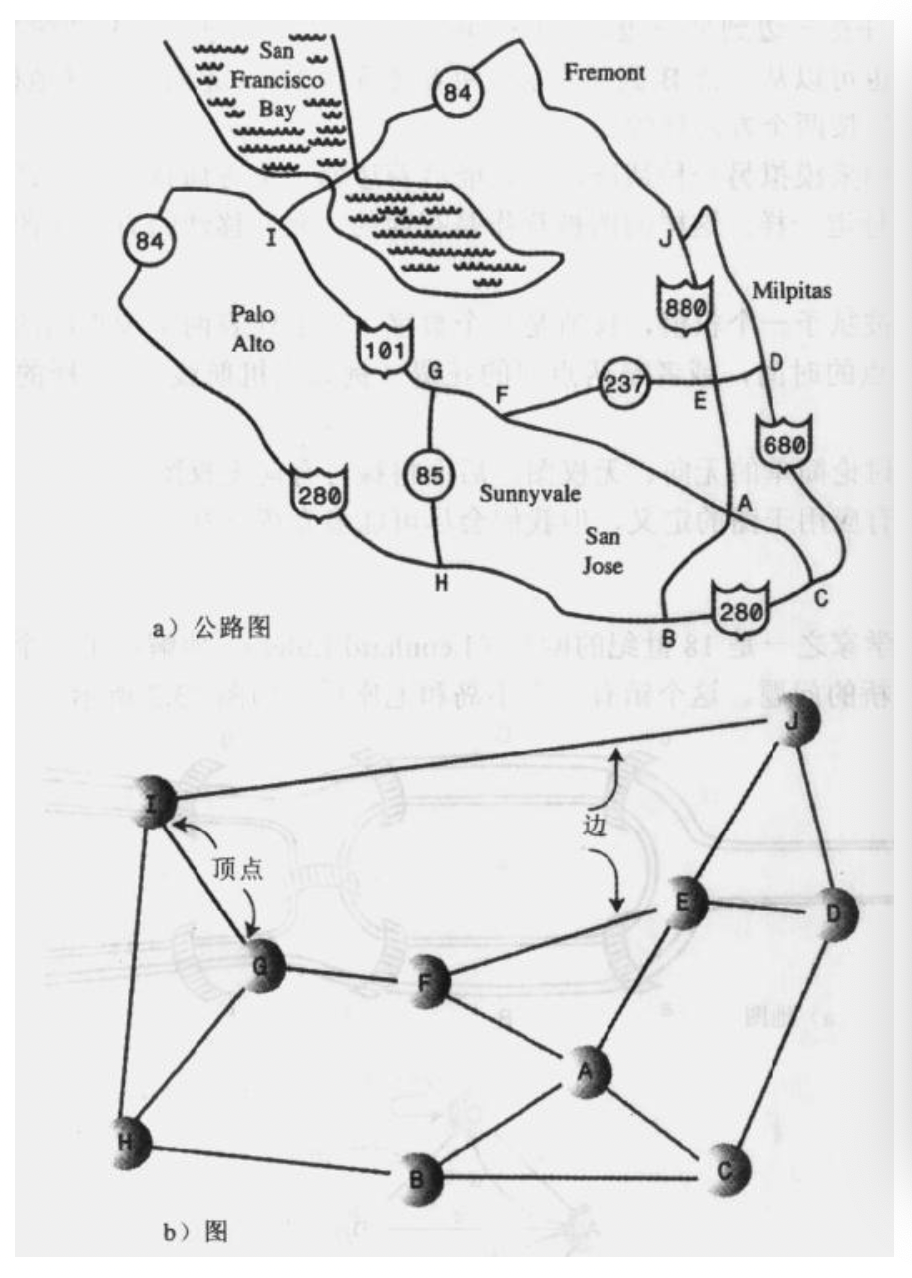
连通图
连通图,如果至少有一条路径可以连接起所有的顶点,那么这个图就被称为连通的。如果没有这样一条路径,就被称为非连通的。
- 非连通的子图可以是连通的。
- 连通
- 非连通
- 连通无环图
- 一类最重要的特殊图
- 许多问题在树上更容易解决
- 其他等效定义:
- 连通图需要n-1条边
- 连通无环图需要n-1条边
- 每对节点之间只有一条路径
- 连通无环图增加一条边就会有环
- 连通图去掉一条边就不再连通
- 一类最重要的特殊图
- 有向连通无环图
- 有向连通无环图(DAG):名字已经说的很清楚
- 等价于节点的有序
- 有向连通无环图(DAG):名字已经说的很清楚
- 二部图
- 节点可以分为两组S和T,这样边只存在于S和T之间(S内或T内没有边)
有向图和无向图
- 可以任意一边到另一边,比如公路上没有设定方向,可以从
A->B,B->A - 有向图就像公路上的双向道
- 设定
A->B , B->A,等价于无向图 - 设定
A->B,则B->A等于在单行道上逆行 - 设定
B->A,则A->B等于在单行道上逆行
有权图和无权图
- 有权图代表着每一条边都不一样,例如不同距离高速收费不同
- 无权图代表每条边都是等价的
存储方式
- 保存集合节点V和集合边E
- 节点可以存储到数组中
- 边必须使用其他方式存储
- 需要支持的操作
- 检索与特定节点关联的所有边
- 检验两个节点是否可以连接
- 使用邻接矩阵或者邻接列表存储边
邻接矩阵
- 一种简单的方式存储连接信息
- 检验两个基点是否连接的时间负责度:O(1)
- 使用 n * n 矩阵 A
- = 1 代表从i到j有边
- = 0 代表从i到j无边
- 使用空间O()内存
- 当n比较小的时候适合使用
- 稠密图比较适合
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| B | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| C | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| D | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
邻接表
- 每一个节点都有向外的边
- 容易迭代某个顶点上的边
- 列表长度可变
- 空间使用O(n + m)

邻接表实现
- 使用链表
- 内存/时间开销过大
- 使用动态分配内存或指针性能好不好
- 使用矢量数组
- 易于编码,没有内存问题
- 但是很慢
- 使用数组(!)
- 假定总边是知道的
- 速度非常快,内存效率也很高
邻接表数组优化
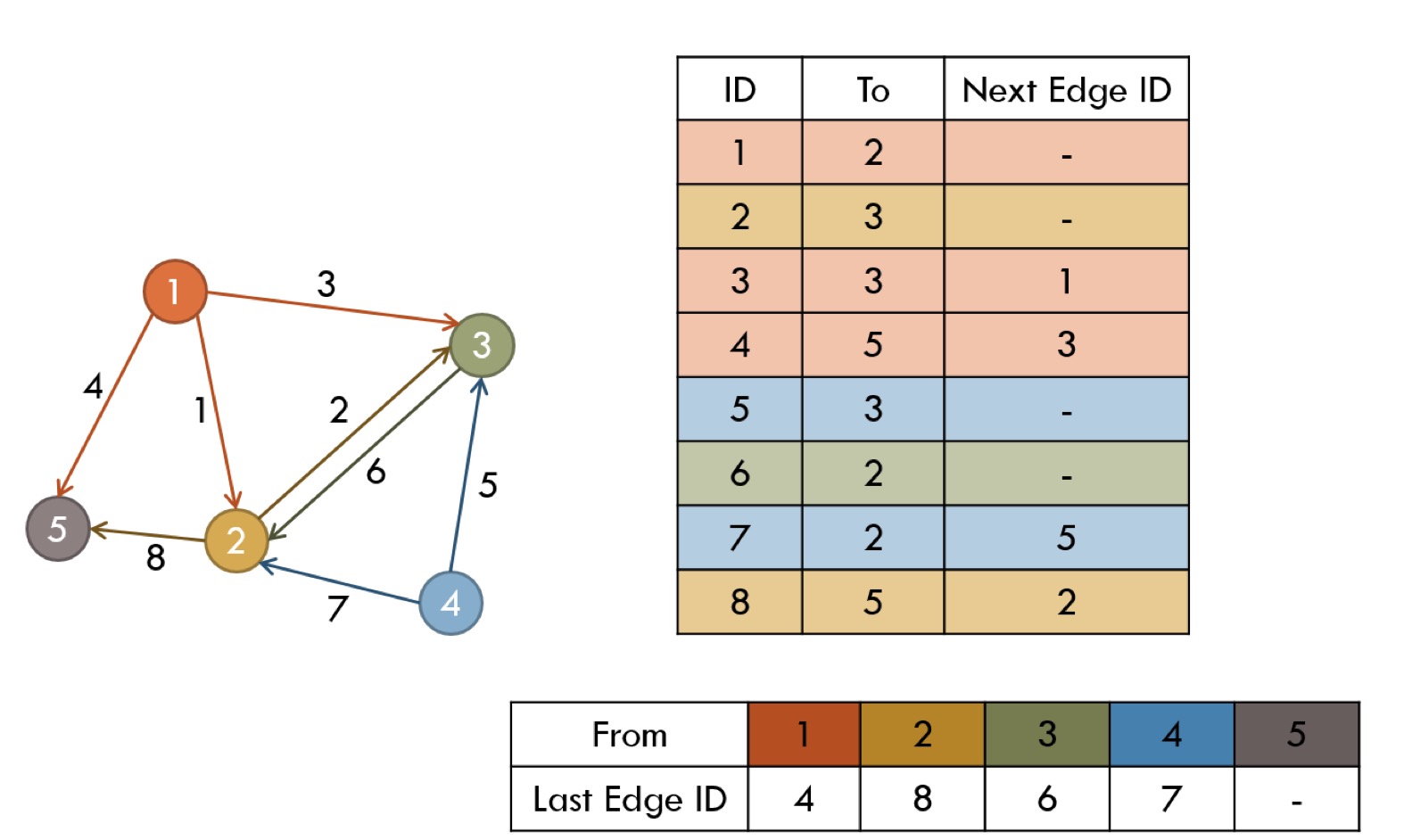
邻接表数组实现
- 使用两个数组,并且数组E的长度问m,数组LE的长度为n
- E包含所有的边
- LE包含开始的顶点和边列表
- 对于数组全部初始化初始化
LE[i]= -1LE[i]=0如果数组是1索引也可以
- 插入一个边从u->v,并使用ID=k
- E[k].to = v
- E[k].nextID = LE[u]
- LE[u] = k
- 迭代从u开始的所有边
for(ID = LE[u]; ID != -1; ID = E[ID].nextID)
// E[ID] is an edge starting from u
- 一旦构建,就很难修改边
- 图必须是静态的
- 增加边很难
代码
邻接矩阵代码
- 编写顶点
type Vertex struct {
// 这里是数据,后面可以转换成对象
label rune
// 是否访问过,在遍历的时候很有用
wasVisited bool
}
func newVertex(label rune) *Vertex {
return &Vertex{label: label, wasVisited: false}
}
- 图结构和初始化图
const MaxVertex int = 20
const LINK int = 1
type Graph struct {
vertexList []*Vertex
adjMat [][]int
nVertex int
}
func newGraph() *Graph {
return &Graph{
vertexList: make([]*Vertex, MaxVertex),
adjMat: make([][]int, MaxVertex, MaxVertex),
nVertex: 0,
}
}
- 新增顶点
func (g *Graph) addVertex(label rune) {
g.nVertex++
g.vertexList[g.nVertex] = newVertex(label)
}
- 连接边
func (g *Graph) addEdge(start, end int) {
g.adjMat[start][end] = LINK
g.adjMat[end][start] = LINK
}
邻接表代码
提示
代码来源于算法4,源码使用邻接表方式编写。
- 数据表现
* % java Graph tinyG.txt
* 13 vertices, 13 edges
* 0: 6 2 1 5
* 1: 0
* 2: 0
* 3: 5 4
* 4: 5 6 3
* 5: 3 4 0
* 6: 0 4
* 7: 8
* 8: 7
* 9: 11 10 12
* 10: 9
* 11: 9 12
* 12: 11 9
- 基础代码,后面使用的Bag其实也就是
List。
public class Bag<Item> implements Iterable<Item> {
private Node<Item> first; // beginning of bag
private int n; // number of elements in bag
// helper linked list class
private static class Node<Item> {
private Item item;
private Node<Item> next;
}
public Bag() {
first = null;
n = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
// 数量
public int size() {
return n;
}
// 增加元素
public void add(Item item) {
Node<Item> oldfirst = first;
first = new Node<Item>();
first.item = item;
first.next = oldfirst;
n++;
}
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {
return new LinkedIterator(first);
}
// 迭代器设计模式
// an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional
private class LinkedIterator implements Iterator<Item> {
private Node<Item> current;
public LinkedIterator(Node<Item> first) {
current = first;
}
public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; }
public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }
public Item next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
Item item = current.item;
current = current.next;
return item;
}
}
}
- 无向图的顶点命名从0~n(n = V-1)
public class Graph {
private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator");
// 命名从0~n,顶点
private final int V;
// 边
private int E;
private Bag<Integer>[] adj;
}
- 无向图有两个主要的操作
- 增加一个边到图中
public void addEdge(int v, int w) {
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
E++;
adj[v].add(w);
adj[w].add(v);
}
- 从一个顶点迭代所有相邻的顶点
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
- 返回顶点的度
public int degree(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
- 查看顶点数量
/**
* 返回这个图中顶点的数量
* Returns the number of vertices in this graph.
*
* @return the number of vertices in this graph
*/
public int V() {
return V;
}
- 查看边数量
/**
* Returns the number of edges in this graph.
*
* @return the number of edges in this graph
*/
public int E() {
return E;
}
- 初始化图
public Graph(int V) {
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices must be non-negative");
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
// 数组长度为V
adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V];
// 数组全部初始化
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>();
}
}
public Graph(In in) {
if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null");
try {
// 数组数量
this.V = in.readInt();
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of vertices in a Graph must be non-negative");
// 初始化
adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>();
}
// 图的边
int E = in.readInt();
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of edges in a Graph must be non-negative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
// 连通两个边
int v = in.readInt();
int w = in.readInt();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
// v w 连通
addEdge(v, w);
}
}
catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in Graph constructor", e);
}
}
// 原型设计模式,深克隆
public Graph(Graph G) {
this.V = G.V();
this.E = G.E();
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices must be non-negative");
// 初始化
// update adjacency lists
adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>();
}
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
// reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original
// 反转原来数据
Stack<Integer> reverse = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int w : G.adj[v]) {
reverse.push(w);
}
// 数据增加到bag中
for (int w : reverse) {
adj[v].add(w);
}
}
}